CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
You can read about kidney disease generally, the categories, symptoms and management here : KIDNEY DISEASE
Chronic kidney disease is a syndrome in which there is progressing, irreversible loss of excretion, endocrine metabolic capacities of the kidney occur as a result of kidney damage. This category of disease is characterized by gradual irreversible deterioration of the kidney. Because the kidney have a large functional reserve, they are able to increase their workload to Meer demands. This means that chronic kidney disease typically progresses over many years without causing symptoms.�

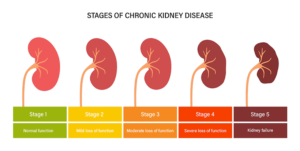
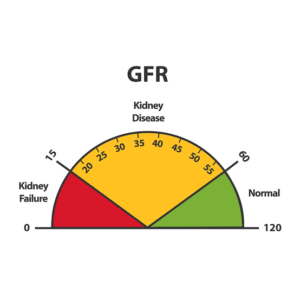
The most common causes of chronic kidney disease also known as CKD are diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Other conditions that can lead to CKD includes inflammation, immunological disease, hereditary disease that directly involve the kidney. Chronic kidney disease is also classified according to estimated GFR (Glomerular filtration rate). This classification is into 5 stages. The stage one is the kidney damage with normal or increased GFR, while the stage two is the mildly decreased GFR. We have the stage 3a and 3b which is the mildly to moderately decreased GFR and moderately to severely decreased GFR respectively. The stage four is the severely decreased GFR while the stage five is kidney failure.
The clinical effects of CKD ranges from the early stages to the advanced stage.The early stages are anorexia ( serious eating disorder), exercise intolerance, fatigue, headache, hypercoagulation, proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine), Hematuria ( blood in urine). The advanced stages include; anemia, bleeding tendency, cardiovascular diseases (diseases related to the heart), confusion and mental impairment, electrolytes imbalance, fluid retention, hormonal abnormalities, metabolic acidosis, muscle wasting, protein energy malnutrition and reduced immunity.
The treatment of chronic kidney disease
The goal of this treatment for patients with CKD is to slow down the progression and prevent alleviate complications. Once the kidney disease reach the final stage, dialysis or kidney transplant is necessary to sustain life. Patients with kidney disease are also closely monitored. Their nutrition intake is closely monitored. There is also reasonable amount of decrease in protein intake. The progression of CKD may slow significantly when following a low protein diet. Fat is the most energy dense macronutrients and is beneficial to malnourished CKD patients especially those on a low protein diet.
Kindly leave comments in the comment section and you can read more on : THE EFFECT OF DIETARY FIBRES ON THE RISK OF TYPE 2 DIABETES





Leave a Reply